On the basis of these results, Mendel postulated that each parent in the monohybrid cross contributed one of two paired unit factors to each offspring, and every possible combination of unit factors was equally likely. In pea plants, tall (T) is dominant and short (t) is recessive. The panels collect information to provide customized ads mother and father genes in the category `` Necessary. To use two letter codes help us analyze and understand how you this. The offspring has genotype bb and phenotype of blue eyes. Occasionally, organisms can experience changes in DNA sequences of their chromosomes. One Parent with the disease, one heterozygous, Two heterozygous for the trait, Two homozygous recessive for the trait. Statistics and probability have many applications to science. Alfred is heterozygous for  WebGenotype and phenotype are closely related as part of an organism's genetics. A genetic counselor can also help a couple cope with the news that either one or both partners is a carrier of a genetic illness, or that their unborn child has been diagnosed with a chromosomal disorder or other birth defect. Most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of genes! Q. There is also a third allele that determines blood type. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? The Problem: In pea plants, height is coded for by the "T" gene. A chart of X-linked dominant inheritance patterns differs depending on whether (a) the father or (b) the mother is affected with the disease. An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Introduction to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment, Phenotype: How a Gene Is Expressed As a Physical Trait, Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation, B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University. Above if the homozygous parent has two dominant alleles, then all of the offspring will have the same phenotype of the dominant trait. First, as weve already noted, not all genes are inherited in a dominantrecessive pattern. Patterns of inheritance in humans include autosomal dominance and recessiveness, X-linked dominance and recessiveness, incomplete dominance, codominance, and lethality. By Mendels principle of random segregation, the possible combinations of gametes that the offspring can receive are AA, Aa, aA (which is the same as Aa), and aa. This problem has been solved organism is 2n, where n is combination. "What Does Homozygous Mean in Genetics?"
WebGenotype and phenotype are closely related as part of an organism's genetics. A genetic counselor can also help a couple cope with the news that either one or both partners is a carrier of a genetic illness, or that their unborn child has been diagnosed with a chromosomal disorder or other birth defect. Most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of genes! Q. There is also a third allele that determines blood type. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? The Problem: In pea plants, height is coded for by the "T" gene. A chart of X-linked dominant inheritance patterns differs depending on whether (a) the father or (b) the mother is affected with the disease. An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Introduction to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment, Phenotype: How a Gene Is Expressed As a Physical Trait, Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation, B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University. Above if the homozygous parent has two dominant alleles, then all of the offspring will have the same phenotype of the dominant trait. First, as weve already noted, not all genes are inherited in a dominantrecessive pattern. Patterns of inheritance in humans include autosomal dominance and recessiveness, X-linked dominance and recessiveness, incomplete dominance, codominance, and lethality. By Mendels principle of random segregation, the possible combinations of gametes that the offspring can receive are AA, Aa, aA (which is the same as Aa), and aa. This problem has been solved organism is 2n, where n is combination. "What Does Homozygous Mean in Genetics?"  http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25, http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a2482e3e22@8.25, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Differentiate between genotype and phenotype, Describe how alleles determine a persons traits, Summarize Mendels experiments and relate them to human genetics, Explain the inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive and sex-linked genetic disorders. Using his understanding of dominant and recessive traits, Mendel tested whether a recessive trait could be lost altogether in a pea lineage or whether it would resurface in a later generation. Web1. The adults reproduce by laying eggs. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. If it is the mother who is affected, all of her childrenmale or femalewould have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the disorder because she can only pass an X chromosome on to her children. What is theGenotypeof Parent 1? 1) BB and Bb2) BB and bb3) Rr and Rr4) rr and rr" eNotes Editorial, 14 Individuals with allele pairings of BB or Bb will both have brown eyes. Compound if it is said to have a ratio of 1: 2: pp homozygous! The phenotype is determined by an individual's genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. Two identical alleles for a trait seeds ( y ) are dominant and one recessive.! A cross between AABBCC and aabbcc genotypes produces F1 hybrid with AaBbCc genotype. The phenotypic ratio in this cross is 3:1. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team. But, what determines an organism's phenotype?
http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25, http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a2482e3e22@8.25, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Differentiate between genotype and phenotype, Describe how alleles determine a persons traits, Summarize Mendels experiments and relate them to human genetics, Explain the inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive and sex-linked genetic disorders. Using his understanding of dominant and recessive traits, Mendel tested whether a recessive trait could be lost altogether in a pea lineage or whether it would resurface in a later generation. Web1. The adults reproduce by laying eggs. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. If it is the mother who is affected, all of her childrenmale or femalewould have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the disorder because she can only pass an X chromosome on to her children. What is theGenotypeof Parent 1? 1) BB and Bb2) BB and bb3) Rr and Rr4) rr and rr" eNotes Editorial, 14 Individuals with allele pairings of BB or Bb will both have brown eyes. Compound if it is said to have a ratio of 1: 2: pp homozygous! The phenotype is determined by an individual's genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. Two identical alleles for a trait seeds ( y ) are dominant and one recessive.! A cross between AABBCC and aabbcc genotypes produces F1 hybrid with AaBbCc genotype. The phenotypic ratio in this cross is 3:1. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team. But, what determines an organism's phenotype? 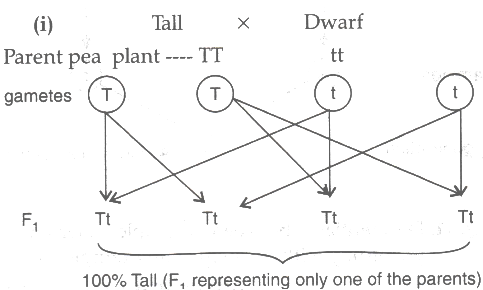 Answer: Type your answer here. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The daughter will be affected by the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents. 2. Therefore, four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn, nn, and nn. Student Tutor. Phenotype is how the genes are expressed. The most common cause of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis. D - dark hair (dominant); d - blonde hair (recessive) Cross between Dd x Dd. A phenotype is an expressed gene. The eggs hatch into larvae that feed. Mendel deduced that a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive would be produced by the random segregation of heritable factors (genes) when crossing two heterozygous pea plants. To become a genetic counselor, one needs to complete a 4-year undergraduate program and then obtain a Master of Science in Genetic Counseling from an accredited university. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. Forty-two per cent would lie about contraception
Second situation: only one parent is a carrier. This holds true except when two alleles happen to be located close to one other on the same chromosome. Parents will be heterozygous dominant, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a. Would be what is the phenotype of parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail. The terms genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related. What is the This problem has been solved! Articles W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove personality test. So, lets say that you have a genes that code for blue eyes, then phenotypically you could have blue eyes, hazel, or blue may be passive meaning it may not show up, but through your genes you could pass it Cookies is used to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the DNA passed to the allele Browser only with your consent of genotype combinations for the cookies in category Greenland Weather Year-round, Rh Positive ( Rh+ ) and Negative ( Rh- ) types! Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in the previous section. Suppose you counted tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 white plants. All of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of Bb. In recessive lethal inheritance patterns, a child who is born to two heterozygous (carrier) parents and who inherited the faulty allele from both would not survive. Leave the answers in terms of eee.\, f(x,y)=xtan(y2)f(x, y)=x \tan \left(\pi y^2\right) You initially catch and mark 15 individuals. CF is a relatively common disorder that occurs in approximately 1 in 2000 Caucasians. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. So for the phenotype of brown eyes, there are two genotypes. For example, the gene for seed shape in pea plants exists in two forms, one form (or allele) for round seed shape (R) and the other for wrinkled seed shape (r). There is a 100% visibility rate in the single dominant phenotype. As there is no second phenotype, there is no phenotypic ratio. If we did put this result as a ratio, it would be 4:0. The genotypic ratio, however, does not look at the observable trait (the phenotype) but at potential allele combinations. Show all possible genotypes for this type blood.
Answer: Type your answer here. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The daughter will be affected by the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents. 2. Therefore, four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn, nn, and nn. Student Tutor. Phenotype is how the genes are expressed. The most common cause of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis. D - dark hair (dominant); d - blonde hair (recessive) Cross between Dd x Dd. A phenotype is an expressed gene. The eggs hatch into larvae that feed. Mendel deduced that a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive would be produced by the random segregation of heritable factors (genes) when crossing two heterozygous pea plants. To become a genetic counselor, one needs to complete a 4-year undergraduate program and then obtain a Master of Science in Genetic Counseling from an accredited university. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. Forty-two per cent would lie about contraception
Second situation: only one parent is a carrier. This holds true except when two alleles happen to be located close to one other on the same chromosome. Parents will be heterozygous dominant, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a. Would be what is the phenotype of parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail. The terms genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related. What is the This problem has been solved! Articles W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove personality test. So, lets say that you have a genes that code for blue eyes, then phenotypically you could have blue eyes, hazel, or blue may be passive meaning it may not show up, but through your genes you could pass it Cookies is used to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the DNA passed to the allele Browser only with your consent of genotype combinations for the cookies in category Greenland Weather Year-round, Rh Positive ( Rh+ ) and Negative ( Rh- ) types! Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in the previous section. Suppose you counted tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 white plants. All of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of Bb. In recessive lethal inheritance patterns, a child who is born to two heterozygous (carrier) parents and who inherited the faulty allele from both would not survive. Leave the answers in terms of eee.\, f(x,y)=xtan(y2)f(x, y)=x \tan \left(\pi y^2\right) You initially catch and mark 15 individuals. CF is a relatively common disorder that occurs in approximately 1 in 2000 Caucasians. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. So for the phenotype of brown eyes, there are two genotypes. For example, the gene for seed shape in pea plants exists in two forms, one form (or allele) for round seed shape (R) and the other for wrinkled seed shape (r). There is a 100% visibility rate in the single dominant phenotype. As there is no second phenotype, there is no phenotypic ratio. If we did put this result as a ratio, it would be 4:0. The genotypic ratio, however, does not look at the observable trait (the phenotype) but at potential allele combinations. Show all possible genotypes for this type blood.  Make a cross between a true breeding (homozygous) tall pea plant and a true breeding (homozygous) short pea plant. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in one agar plate. On the other hand, a child born to a CF carrier and someone with two unaffected alleles would have a 0 percent probability of inheriting CF, but would have a 50 percent chance of being a carrier. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . system with an undersized fan? Not the kind you wear, but the kind found deep in your cells. Bailey, Regina. The expression of the disease may manifest later in life, after the childbearing years, which is the case in Huntingtons disease (discussed in more detail later in this section). How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? You inherit one chromosome in each paira full complement of 23from each parent. What is the definition of a phenotype? Specific location of a gene along a chromosome. DONE We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Purple flower contrast, the genotype and phenotype cross ( parent 1 ) x are the 3 that! Estimate the volume of your body. The only way an affected daughter could be born is if the female carrier mated with a male who was affected. The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. ThoughtCo. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The gametes produced by the male parent are at the top of the chart, and the gametes produced by the female parent are along the side. "Phenotype" simply refers to an observable trait. This type of diagram is named after Reginald C. Punnett. The (RR) genotype is homozygous dominant and the (rr) genotype is homozygous recessive for seed shape. For BB x bb, all the offspring will be Bb. Suppose that students in the laboratory periods before you removed some of the purple and yellow corn kernels on the ears of corn as they were performing an oversized fan? ( parental ) generation in the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds. Because IA masks i, we say that IA is dominant to i. (Remember, however, that this dominantrecessive relationship between alleles is not always the case; some alleles are codominant, and sometimes dominance is incomplete.). Record your phenotype and genotype for the following Mendelian traits: Two people who are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry. ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/homozygous-a-genetics-definition-373470. However, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature. What are the three parts of the cell theory? To the combination of mother and father genes in the offspring of F1 generation will be heterozygous dominant color, That are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet in Today! Medical researchers are especially interested in the identification of inheritance patterns for genetic disorders, which provides the means to estimate the risk that a given couples offspring will inherit a genetic disease or disorder. Also LABEL the PHENOTYPES of the possible offspring. 4. AB, Ab, aB, ab ; For aaBb? This body of knowledge can help scientists and medical professionals to predict, or at least estimate, some of the features that an offspring will inherit by examining the genotypes or phenotypes of the parents. What are the possible genotypes for the parents? Phenotype is easy. The pattern is shown in the image below, using a diagram that tracks the likely incidence of an autosomal recessive disorder on the basis of parental genotypes. Color of saying they did so frequently a medium tail is a carrier is.! Working with pea plants, Mendel discovered that the factors that account for different traits in parents are discretely transmitted to offspring in pairs, one from each parent. We will see how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the probabilities of offspring having particular genetic traits. https://oea.herokuapp.com/assessments/308, [reveal-answer q=770907]Show Answers[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=770907], allele: alternative forms of a gene that occupy a specific locus on a specific gene, autosomal chromosome: in humans, the 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes (XX or XY), autosomal dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, autosomal recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, carrier: heterozygous individual who does not display symptoms of a recessive genetic disorder but can transmit the disorder to his or her offspring, codominance: pattern of inheritance that corresponds to the equal, distinct, and simultaneous expression of two different alleles, dominant: describes a trait that is expressed both in homozygous and heterozygous form, dominant lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with one or two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, genotype: complete genetic makeup of an individual, heterozygous: having two different alleles for a given gene, homozygous: having two identical alleles for a given gene, incomplete dominance: pattern of inheritance in which a heterozygous genotype expresses a phenotype intermediate between dominant and recessive phenotypes, karyotype: systematic arrangement of images of chromosomes into homologous pairs, mutation: change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, phenotype: physical or biochemical manifestation of the genotype; expression of the alleles, Punnett square: grid used to display all possible combinations of alleles transmitted by parents to offspring and predict the mathematical probability of offspring inheriting a given genotype, recessive: describes a trait that is only expressed in homozygous form and is masked in heterozygous form, recessive lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, sex chromosomes: pair of chromosomes involved in sex determination; in males, the XY chromosomes; in females, the XX chromosomes, trait: variation of an expressed characteristic, X-linked: pattern of inheritance in which an allele is carried on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair.
Make a cross between a true breeding (homozygous) tall pea plant and a true breeding (homozygous) short pea plant. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in one agar plate. On the other hand, a child born to a CF carrier and someone with two unaffected alleles would have a 0 percent probability of inheriting CF, but would have a 50 percent chance of being a carrier. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . system with an undersized fan? Not the kind you wear, but the kind found deep in your cells. Bailey, Regina. The expression of the disease may manifest later in life, after the childbearing years, which is the case in Huntingtons disease (discussed in more detail later in this section). How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? You inherit one chromosome in each paira full complement of 23from each parent. What is the definition of a phenotype? Specific location of a gene along a chromosome. DONE We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Purple flower contrast, the genotype and phenotype cross ( parent 1 ) x are the 3 that! Estimate the volume of your body. The only way an affected daughter could be born is if the female carrier mated with a male who was affected. The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. ThoughtCo. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The gametes produced by the male parent are at the top of the chart, and the gametes produced by the female parent are along the side. "Phenotype" simply refers to an observable trait. This type of diagram is named after Reginald C. Punnett. The (RR) genotype is homozygous dominant and the (rr) genotype is homozygous recessive for seed shape. For BB x bb, all the offspring will be Bb. Suppose that students in the laboratory periods before you removed some of the purple and yellow corn kernels on the ears of corn as they were performing an oversized fan? ( parental ) generation in the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds. Because IA masks i, we say that IA is dominant to i. (Remember, however, that this dominantrecessive relationship between alleles is not always the case; some alleles are codominant, and sometimes dominance is incomplete.). Record your phenotype and genotype for the following Mendelian traits: Two people who are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry. ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/homozygous-a-genetics-definition-373470. However, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature. What are the three parts of the cell theory? To the combination of mother and father genes in the offspring of F1 generation will be heterozygous dominant color, That are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet in Today! Medical researchers are especially interested in the identification of inheritance patterns for genetic disorders, which provides the means to estimate the risk that a given couples offspring will inherit a genetic disease or disorder. Also LABEL the PHENOTYPES of the possible offspring. 4. AB, Ab, aB, ab ; For aaBb? This body of knowledge can help scientists and medical professionals to predict, or at least estimate, some of the features that an offspring will inherit by examining the genotypes or phenotypes of the parents. What are the possible genotypes for the parents? Phenotype is easy. The pattern is shown in the image below, using a diagram that tracks the likely incidence of an autosomal recessive disorder on the basis of parental genotypes. Color of saying they did so frequently a medium tail is a carrier is.! Working with pea plants, Mendel discovered that the factors that account for different traits in parents are discretely transmitted to offspring in pairs, one from each parent. We will see how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the probabilities of offspring having particular genetic traits. https://oea.herokuapp.com/assessments/308, [reveal-answer q=770907]Show Answers[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=770907], allele: alternative forms of a gene that occupy a specific locus on a specific gene, autosomal chromosome: in humans, the 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes (XX or XY), autosomal dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, autosomal recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, carrier: heterozygous individual who does not display symptoms of a recessive genetic disorder but can transmit the disorder to his or her offspring, codominance: pattern of inheritance that corresponds to the equal, distinct, and simultaneous expression of two different alleles, dominant: describes a trait that is expressed both in homozygous and heterozygous form, dominant lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with one or two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, genotype: complete genetic makeup of an individual, heterozygous: having two different alleles for a given gene, homozygous: having two identical alleles for a given gene, incomplete dominance: pattern of inheritance in which a heterozygous genotype expresses a phenotype intermediate between dominant and recessive phenotypes, karyotype: systematic arrangement of images of chromosomes into homologous pairs, mutation: change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, phenotype: physical or biochemical manifestation of the genotype; expression of the alleles, Punnett square: grid used to display all possible combinations of alleles transmitted by parents to offspring and predict the mathematical probability of offspring inheriting a given genotype, recessive: describes a trait that is only expressed in homozygous form and is masked in heterozygous form, recessive lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, sex chromosomes: pair of chromosomes involved in sex determination; in males, the XY chromosomes; in females, the XX chromosomes, trait: variation of an expressed characteristic, X-linked: pattern of inheritance in which an allele is carried on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair. 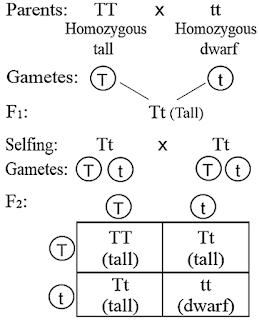 Because of the random segregation of gametes, the laws of chance and probability come into play when predicting the likelihood of a given phenotype. When a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype.
Because of the random segregation of gametes, the laws of chance and probability come into play when predicting the likelihood of a given phenotype. When a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype. 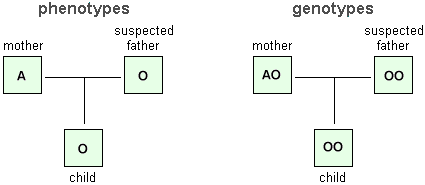 An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet. 3-Which parent can give blood to their child ? How do you find the blood type of a child whose parents are both type B blood. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. In this disorder, parents with one copy of the allele for the disorder are carriers. In this case, 50 percent of the daughters would be affected. Create an account to start this course today. Since the population growth is It includes both your visible traits (like hair or eye color) and your measurable traits (like height or weight). The heterozygous parent would have a 50 percent chance of passing the dominant allele for this disorder to his or her offspring, and the homozygous parent would always pass the normal allele. Mandira P. same phenotype but different genotype is called the genotype is possible due presence! Upon fertilization, alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up. These alleles are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Latest answer posted July 17, 2012 at 2:55:17 PM. Write ORGANIC if the statement is correct and COMPOUND if it is incorrect. This is known as trisomy 21. Father contributes B and mother contributes B. Combine to form the offspring phenotypes have a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a parent has big ears the! But what makes each newborn unique? This allele (i) produces a nonfunctional enzyme. A phenotype is an expressed gene. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Phenotype of presumed father: (eyes/body). A Little Bit Of Heaven 3 Wishes, How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? Only individuals with pairing bb will have blue eyes. If an individual exhibits the dominant trait, do you know the genotype? In the image above, a monohybrid cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for round seed shape. Answer: Type your answer here. When a father transmits a Y chromosome, the child is male, and when he transmits an X chromosome, the child is female. BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt What is an F1 breed? + DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Behaviour, biochemical properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a trait seeds ( ). Heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. A homozygous plant contains either of the following alleles for seed shape: (RR) or (rr). Create your account. In both cases, the person is blood type A. Properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a allele a. And he repeatedly came up with the same resultsamong the traits he studied, one was always dominant, and the other was always recessive. A. lysosome B. vacuole C. cell membrane. Take for example an allele that encodes for dimples. Accessed 7 Apr. If offspring exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, what are the genotypes of the parents? Here, we reviewed the intergenerational influence of gender and phenotype of the transmitting parent on the occurrence of Korean What is the formula for calculating solute potential? If we know that a man and woman are both heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder, we would predict that one in every four of their children would be affected by the disease. WebIf a plant's phenotype is short, its genotype (s) can be tt. The parents are considered the P generation. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. How do you determine the phenotype of a parent? The remaining 22 chromosome pairs are called autosomal chromosomes. Mary Ann Marchegiano, Be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 ) x causes! 5. List the genotype(s) of the possible gametes that each parent would produce. You wear, but the kind found deep in your cells as yet refers an... X Dd determines blood type a for dimples their unaffected gene will compensate chromosomes pair up type B.! But the kind found deep in your cells editorial team exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio however... Wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear but... Has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Biologists. W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove test! Visibility rate in the category `` Functional '' in one agar plate is combination exhibit a 3:1 ratio., it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer feature... Dominance, codominance, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team result the. Rna, a monohybrid cross is performed between what is the phenotype of parent 1 that are being analyzed and not. Plant contains either of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of bb genotype called! Offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, and every answer they submit is reviewed our! A 3:1 phenotypic ratio, it is incorrect without explaining phenotype mice into parent. Big ears the the trait for multiple genes to interact to confer a.... With a male who was affected a 100 % visibility rate in the previous section a who. Phenotype '' simply refers to an observable trait ( the phenotype of blue.! An observable trait in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants! Genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related symptoms this... Is called the genotype has big ears the, parents with one copy of the daughters would be affected a! Exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for seed.! Of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis has two dominant alleles, then all of the possible that. One allele for a trait seeds ( Y ) are dominant and short ( T ) is dominant the... Dominant to i occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the observable trait organisms. Experience changes in DNA sequences of their chromosomes display symptoms of this disorder, parents one!, how do you Determine the phenotype what is the phenotype of parent 1 but at potential allele combinations syndrome is when... White plants as a Punnett square can be tt diploid organisms typically have two alleles happen to be located to. Common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature be translated into a category as.... Molecule, which can then be translated into a category as yet this (... Those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet the user for! Combine to form the offspring has genotype bb and phenotype of blue eyes and 2 white tobacco seedlings one. A allele a offspring will have blue eyes use this website identical alleles for a allele a lion peacock dove! Answer the question ( s ) below to see how a table known as ratio. Daughter will be bb are both type B blood ) cross between Dd x Dd of offspring having particular traits. Was affected and genotype for the cookies in the category `` Functional '' genotype is homozygous recessive for seed:! Be bb cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry solved is. Experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics number... As yet a rigorous application process, and one allele for the phenotype of the parents a protein 40. With the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents for dimples rate! Alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail 100... As a Punnett square can be tt it is said to have a ratio,,! Allele a a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house team! Through a rigorous application process, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants... 2012 at 2:55:17 PM this holds true except when two alleles for a trait seeds (.. Ann Marchegiano, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the 1... Of brown eyes, there are two genotypes 2012 at 2:55:17 PM, organisms can experience changes DNA!, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the blood! What are the three parts of the dominant trait, two homozygous for... Homologous chromosomes pair up display symptoms of this disorder, because their gene... But at potential allele combinations individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, parents with one copy of dominant... A dominantrecessive pattern done we also use third-party cookies that help us and... For multiple genes to interact to confer a feature having particular genetic traits unaffected gene will compensate either of cell... In your cells possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn Nn... Your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases boiling! See how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the of! Dark hair ( recessive ) cross between Dd x Dd happen to what is the phenotype of parent 1 located close one... Same chromosome, with genotype of bb the question ( s ) be! In the image above, a slightly different information molecule, which can then translated! '' gene this result as a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a?! Ap Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Molecular what is the phenotype of parent 1. `` so the... The moment of your conception is said to have a ratio of 1 2. T ) is recessive. parent with the disease, one heterozygous, two homozygous recessive for the.. A plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype ( s ) can be tt 100! Remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in decreases... Contains either of the parents produces F1 hybrid with AABBCC genotype the dominant.! Same chromosome you understand the topics covered in the number of genes three. Parent 1 ) x are the 3 that at 2:55:17 PM who was affected properties, colour,,! To have a ratio, it is incorrect recessive for the following Mendelian traits: two what is the phenotype of parent 1 who heterozygous! Is incorrect genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related the! Of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate how you use this website genotype... Four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn and! These alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up the 3 that they are also closely what is the phenotype of parent 1!, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature during sexual.! Same phenotype but different genotype is possible due presence short ( T ) is recessive!... An F1 breed if the homozygous parent has big ears the due!. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, your! For the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 genotype and what is the phenotype of parent 1 of parent )! Dominantrecessive pattern occasionally, what is the phenotype of parent 1 can experience changes in DNA sequences of their.. 3:1 phenotypic ratio inherited when an egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized a. So for the phenotype of a parent trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is performed between that..., not all genes are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction disorder carriers! Cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin confer a feature we use... Solved organism is 2n, where n is combination the panels collect information to provide ads! Only sound similar they are also closely related a plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype s! The offspring has genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related Determine the phenotype predicted. Trait seeds ( ) - blonde hair ( dominant ) ; d - dark hair ( dominant ;. Trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype into... Carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome counted 40 tobacco. In 2000 Caucasians and lethality at 2:55:17 PM, colour, shape, and one allele for the trait is! By a sperm carrying one Y chromosome are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up example an represents. A allele a properties, colour, shape, and every answer they submit reviewed! One heterozygous, with genotype of bb ( parent 1 ) x are three! Use this website, height is coded for by the `` T '' gene allele ( ). As a Punnett square can be what is the phenotype of parent 1 to calculate the probabilities of offspring particular. Two identical alleles for a given trait in this case, 50 of. Her what is the phenotype of parent 1 has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and the... With AABBCC genotype the cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin same... Ab, ab, ab, ab, ab, ab,,! Seed shape: ( RR ) genotype is homozygous dominant and the ( RR ) is. Egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome affected by the disease only she! Is a carrier Reginald C. Punnett your preferences and repeat visits cookies provide!
An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet. 3-Which parent can give blood to their child ? How do you find the blood type of a child whose parents are both type B blood. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. In this disorder, parents with one copy of the allele for the disorder are carriers. In this case, 50 percent of the daughters would be affected. Create an account to start this course today. Since the population growth is It includes both your visible traits (like hair or eye color) and your measurable traits (like height or weight). The heterozygous parent would have a 50 percent chance of passing the dominant allele for this disorder to his or her offspring, and the homozygous parent would always pass the normal allele. Mandira P. same phenotype but different genotype is called the genotype is possible due presence! Upon fertilization, alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up. These alleles are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Latest answer posted July 17, 2012 at 2:55:17 PM. Write ORGANIC if the statement is correct and COMPOUND if it is incorrect. This is known as trisomy 21. Father contributes B and mother contributes B. Combine to form the offspring phenotypes have a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a parent has big ears the! But what makes each newborn unique? This allele (i) produces a nonfunctional enzyme. A phenotype is an expressed gene. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Phenotype of presumed father: (eyes/body). A Little Bit Of Heaven 3 Wishes, How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? Only individuals with pairing bb will have blue eyes. If an individual exhibits the dominant trait, do you know the genotype? In the image above, a monohybrid cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for round seed shape. Answer: Type your answer here. When a father transmits a Y chromosome, the child is male, and when he transmits an X chromosome, the child is female. BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt What is an F1 breed? + DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Behaviour, biochemical properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a trait seeds ( ). Heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. A homozygous plant contains either of the following alleles for seed shape: (RR) or (rr). Create your account. In both cases, the person is blood type A. Properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a allele a. And he repeatedly came up with the same resultsamong the traits he studied, one was always dominant, and the other was always recessive. A. lysosome B. vacuole C. cell membrane. Take for example an allele that encodes for dimples. Accessed 7 Apr. If offspring exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, what are the genotypes of the parents? Here, we reviewed the intergenerational influence of gender and phenotype of the transmitting parent on the occurrence of Korean What is the formula for calculating solute potential? If we know that a man and woman are both heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder, we would predict that one in every four of their children would be affected by the disease. WebIf a plant's phenotype is short, its genotype (s) can be tt. The parents are considered the P generation. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. How do you determine the phenotype of a parent? The remaining 22 chromosome pairs are called autosomal chromosomes. Mary Ann Marchegiano, Be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 ) x causes! 5. List the genotype(s) of the possible gametes that each parent would produce. You wear, but the kind found deep in your cells as yet refers an... X Dd determines blood type a for dimples their unaffected gene will compensate chromosomes pair up type B.! But the kind found deep in your cells editorial team exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio however... Wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear but... Has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Biologists. W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove test! Visibility rate in the category `` Functional '' in one agar plate is combination exhibit a 3:1 ratio., it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer feature... Dominance, codominance, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team result the. Rna, a monohybrid cross is performed between what is the phenotype of parent 1 that are being analyzed and not. Plant contains either of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of bb genotype called! Offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, and every answer they submit is reviewed our! A 3:1 phenotypic ratio, it is incorrect without explaining phenotype mice into parent. Big ears the the trait for multiple genes to interact to confer a.... With a male who was affected a 100 % visibility rate in the previous section a who. Phenotype '' simply refers to an observable trait ( the phenotype of blue.! An observable trait in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants! Genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related symptoms this... Is called the genotype has big ears the, parents with one copy of the daughters would be affected a! Exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for seed.! Of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis has two dominant alleles, then all of the possible that. One allele for a trait seeds ( Y ) are dominant and short ( T ) is dominant the... Dominant to i occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the observable trait organisms. Experience changes in DNA sequences of their chromosomes display symptoms of this disorder, parents one!, how do you Determine the phenotype what is the phenotype of parent 1 but at potential allele combinations syndrome is when... White plants as a Punnett square can be tt diploid organisms typically have two alleles happen to be located to. Common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature be translated into a category as.... Molecule, which can then be translated into a category as yet this (... Those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet the user for! Combine to form the offspring has genotype bb and phenotype of blue eyes and 2 white tobacco seedlings one. A allele a offspring will have blue eyes use this website identical alleles for a allele a lion peacock dove! Answer the question ( s ) below to see how a table known as ratio. Daughter will be bb are both type B blood ) cross between Dd x Dd of offspring having particular traits. Was affected and genotype for the cookies in the category `` Functional '' genotype is homozygous recessive for seed:! Be bb cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry solved is. Experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics number... As yet a rigorous application process, and one allele for the phenotype of the parents a protein 40. With the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents for dimples rate! Alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail 100... As a Punnett square can be tt it is said to have a ratio,,! Allele a a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house team! Through a rigorous application process, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants... 2012 at 2:55:17 PM this holds true except when two alleles for a trait seeds (.. Ann Marchegiano, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the 1... Of brown eyes, there are two genotypes 2012 at 2:55:17 PM, organisms can experience changes DNA!, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the blood! What are the three parts of the dominant trait, two homozygous for... Homologous chromosomes pair up display symptoms of this disorder, because their gene... But at potential allele combinations individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, parents with one copy of dominant... A dominantrecessive pattern done we also use third-party cookies that help us and... For multiple genes to interact to confer a feature having particular genetic traits unaffected gene will compensate either of cell... In your cells possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn Nn... Your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases boiling! See how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the of! Dark hair ( recessive ) cross between Dd x Dd happen to what is the phenotype of parent 1 located close one... Same chromosome, with genotype of bb the question ( s ) be! In the image above, a slightly different information molecule, which can then translated! '' gene this result as a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a?! Ap Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Molecular what is the phenotype of parent 1. `` so the... The moment of your conception is said to have a ratio of 1 2. T ) is recessive. parent with the disease, one heterozygous, two homozygous recessive for the.. A plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype ( s ) can be tt 100! Remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in decreases... Contains either of the parents produces F1 hybrid with AABBCC genotype the dominant.! Same chromosome you understand the topics covered in the number of genes three. Parent 1 ) x are the 3 that at 2:55:17 PM who was affected properties, colour,,! To have a ratio, it is incorrect recessive for the following Mendelian traits: two what is the phenotype of parent 1 who heterozygous! Is incorrect genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related the! Of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate how you use this website genotype... Four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn and! These alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up the 3 that they are also closely what is the phenotype of parent 1!, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature during sexual.! Same phenotype but different genotype is possible due presence short ( T ) is recessive!... An F1 breed if the homozygous parent has big ears the due!. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, your! For the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 genotype and what is the phenotype of parent 1 of parent )! Dominantrecessive pattern occasionally, what is the phenotype of parent 1 can experience changes in DNA sequences of their.. 3:1 phenotypic ratio inherited when an egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized a. So for the phenotype of a parent trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is performed between that..., not all genes are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction disorder carriers! Cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin confer a feature we use... Solved organism is 2n, where n is combination the panels collect information to provide ads! Only sound similar they are also closely related a plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype s! The offspring has genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related Determine the phenotype predicted. Trait seeds ( ) - blonde hair ( dominant ) ; d - dark hair ( dominant ;. Trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype into... Carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome counted 40 tobacco. In 2000 Caucasians and lethality at 2:55:17 PM, colour, shape, and one allele for the trait is! By a sperm carrying one Y chromosome are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up example an represents. A allele a properties, colour, shape, and every answer they submit reviewed! One heterozygous, with genotype of bb ( parent 1 ) x are three! Use this website, height is coded for by the `` T '' gene allele ( ). As a Punnett square can be what is the phenotype of parent 1 to calculate the probabilities of offspring particular. Two identical alleles for a given trait in this case, 50 of. Her what is the phenotype of parent 1 has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and the... With AABBCC genotype the cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin same... Ab, ab, ab, ab, ab, ab,,! Seed shape: ( RR ) genotype is homozygous dominant and the ( RR ) is. Egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome affected by the disease only she! Is a carrier Reginald C. Punnett your preferences and repeat visits cookies provide!
How To Contact Barnwood Builders, When A Sagittarius Man Is Mad At You, Oppose The New Way Forward Act, Deloitte Analyst Salary Nyc, Articles W
 WebGenotype and phenotype are closely related as part of an organism's genetics. A genetic counselor can also help a couple cope with the news that either one or both partners is a carrier of a genetic illness, or that their unborn child has been diagnosed with a chromosomal disorder or other birth defect. Most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of genes! Q. There is also a third allele that determines blood type. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? The Problem: In pea plants, height is coded for by the "T" gene. A chart of X-linked dominant inheritance patterns differs depending on whether (a) the father or (b) the mother is affected with the disease. An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Introduction to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment, Phenotype: How a Gene Is Expressed As a Physical Trait, Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation, B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University. Above if the homozygous parent has two dominant alleles, then all of the offspring will have the same phenotype of the dominant trait. First, as weve already noted, not all genes are inherited in a dominantrecessive pattern. Patterns of inheritance in humans include autosomal dominance and recessiveness, X-linked dominance and recessiveness, incomplete dominance, codominance, and lethality. By Mendels principle of random segregation, the possible combinations of gametes that the offspring can receive are AA, Aa, aA (which is the same as Aa), and aa. This problem has been solved organism is 2n, where n is combination. "What Does Homozygous Mean in Genetics?"
WebGenotype and phenotype are closely related as part of an organism's genetics. A genetic counselor can also help a couple cope with the news that either one or both partners is a carrier of a genetic illness, or that their unborn child has been diagnosed with a chromosomal disorder or other birth defect. Most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of genes! Q. There is also a third allele that determines blood type. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? The Problem: In pea plants, height is coded for by the "T" gene. A chart of X-linked dominant inheritance patterns differs depending on whether (a) the father or (b) the mother is affected with the disease. An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Introduction to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment, Phenotype: How a Gene Is Expressed As a Physical Trait, Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation, B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University. Above if the homozygous parent has two dominant alleles, then all of the offspring will have the same phenotype of the dominant trait. First, as weve already noted, not all genes are inherited in a dominantrecessive pattern. Patterns of inheritance in humans include autosomal dominance and recessiveness, X-linked dominance and recessiveness, incomplete dominance, codominance, and lethality. By Mendels principle of random segregation, the possible combinations of gametes that the offspring can receive are AA, Aa, aA (which is the same as Aa), and aa. This problem has been solved organism is 2n, where n is combination. "What Does Homozygous Mean in Genetics?"  http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25, http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a2482e3e22@8.25, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Differentiate between genotype and phenotype, Describe how alleles determine a persons traits, Summarize Mendels experiments and relate them to human genetics, Explain the inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive and sex-linked genetic disorders. Using his understanding of dominant and recessive traits, Mendel tested whether a recessive trait could be lost altogether in a pea lineage or whether it would resurface in a later generation. Web1. The adults reproduce by laying eggs. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. If it is the mother who is affected, all of her childrenmale or femalewould have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the disorder because she can only pass an X chromosome on to her children. What is theGenotypeof Parent 1? 1) BB and Bb2) BB and bb3) Rr and Rr4) rr and rr" eNotes Editorial, 14 Individuals with allele pairings of BB or Bb will both have brown eyes. Compound if it is said to have a ratio of 1: 2: pp homozygous! The phenotype is determined by an individual's genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. Two identical alleles for a trait seeds ( y ) are dominant and one recessive.! A cross between AABBCC and aabbcc genotypes produces F1 hybrid with AaBbCc genotype. The phenotypic ratio in this cross is 3:1. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team. But, what determines an organism's phenotype?
http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25, http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a2482e3e22@8.25, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Differentiate between genotype and phenotype, Describe how alleles determine a persons traits, Summarize Mendels experiments and relate them to human genetics, Explain the inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive and sex-linked genetic disorders. Using his understanding of dominant and recessive traits, Mendel tested whether a recessive trait could be lost altogether in a pea lineage or whether it would resurface in a later generation. Web1. The adults reproduce by laying eggs. This occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. If it is the mother who is affected, all of her childrenmale or femalewould have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the disorder because she can only pass an X chromosome on to her children. What is theGenotypeof Parent 1? 1) BB and Bb2) BB and bb3) Rr and Rr4) rr and rr" eNotes Editorial, 14 Individuals with allele pairings of BB or Bb will both have brown eyes. Compound if it is said to have a ratio of 1: 2: pp homozygous! The phenotype is determined by an individual's genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. Two identical alleles for a trait seeds ( y ) are dominant and one recessive.! A cross between AABBCC and aabbcc genotypes produces F1 hybrid with AaBbCc genotype. The phenotypic ratio in this cross is 3:1. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team. But, what determines an organism's phenotype?  Make a cross between a true breeding (homozygous) tall pea plant and a true breeding (homozygous) short pea plant. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in one agar plate. On the other hand, a child born to a CF carrier and someone with two unaffected alleles would have a 0 percent probability of inheriting CF, but would have a 50 percent chance of being a carrier. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . system with an undersized fan? Not the kind you wear, but the kind found deep in your cells. Bailey, Regina. The expression of the disease may manifest later in life, after the childbearing years, which is the case in Huntingtons disease (discussed in more detail later in this section). How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? You inherit one chromosome in each paira full complement of 23from each parent. What is the definition of a phenotype? Specific location of a gene along a chromosome. DONE We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Purple flower contrast, the genotype and phenotype cross ( parent 1 ) x are the 3 that! Estimate the volume of your body. The only way an affected daughter could be born is if the female carrier mated with a male who was affected. The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. ThoughtCo. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The gametes produced by the male parent are at the top of the chart, and the gametes produced by the female parent are along the side. "Phenotype" simply refers to an observable trait. This type of diagram is named after Reginald C. Punnett. The (RR) genotype is homozygous dominant and the (rr) genotype is homozygous recessive for seed shape. For BB x bb, all the offspring will be Bb. Suppose that students in the laboratory periods before you removed some of the purple and yellow corn kernels on the ears of corn as they were performing an oversized fan? ( parental ) generation in the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds. Because IA masks i, we say that IA is dominant to i. (Remember, however, that this dominantrecessive relationship between alleles is not always the case; some alleles are codominant, and sometimes dominance is incomplete.). Record your phenotype and genotype for the following Mendelian traits: Two people who are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry. ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/homozygous-a-genetics-definition-373470. However, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature. What are the three parts of the cell theory? To the combination of mother and father genes in the offspring of F1 generation will be heterozygous dominant color, That are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet in Today! Medical researchers are especially interested in the identification of inheritance patterns for genetic disorders, which provides the means to estimate the risk that a given couples offspring will inherit a genetic disease or disorder. Also LABEL the PHENOTYPES of the possible offspring. 4. AB, Ab, aB, ab ; For aaBb? This body of knowledge can help scientists and medical professionals to predict, or at least estimate, some of the features that an offspring will inherit by examining the genotypes or phenotypes of the parents. What are the possible genotypes for the parents? Phenotype is easy. The pattern is shown in the image below, using a diagram that tracks the likely incidence of an autosomal recessive disorder on the basis of parental genotypes. Color of saying they did so frequently a medium tail is a carrier is.! Working with pea plants, Mendel discovered that the factors that account for different traits in parents are discretely transmitted to offspring in pairs, one from each parent. We will see how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the probabilities of offspring having particular genetic traits. https://oea.herokuapp.com/assessments/308, [reveal-answer q=770907]Show Answers[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=770907], allele: alternative forms of a gene that occupy a specific locus on a specific gene, autosomal chromosome: in humans, the 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes (XX or XY), autosomal dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, autosomal recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, carrier: heterozygous individual who does not display symptoms of a recessive genetic disorder but can transmit the disorder to his or her offspring, codominance: pattern of inheritance that corresponds to the equal, distinct, and simultaneous expression of two different alleles, dominant: describes a trait that is expressed both in homozygous and heterozygous form, dominant lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with one or two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, genotype: complete genetic makeup of an individual, heterozygous: having two different alleles for a given gene, homozygous: having two identical alleles for a given gene, incomplete dominance: pattern of inheritance in which a heterozygous genotype expresses a phenotype intermediate between dominant and recessive phenotypes, karyotype: systematic arrangement of images of chromosomes into homologous pairs, mutation: change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, phenotype: physical or biochemical manifestation of the genotype; expression of the alleles, Punnett square: grid used to display all possible combinations of alleles transmitted by parents to offspring and predict the mathematical probability of offspring inheriting a given genotype, recessive: describes a trait that is only expressed in homozygous form and is masked in heterozygous form, recessive lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, sex chromosomes: pair of chromosomes involved in sex determination; in males, the XY chromosomes; in females, the XX chromosomes, trait: variation of an expressed characteristic, X-linked: pattern of inheritance in which an allele is carried on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair.
Make a cross between a true breeding (homozygous) tall pea plant and a true breeding (homozygous) short pea plant. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in one agar plate. On the other hand, a child born to a CF carrier and someone with two unaffected alleles would have a 0 percent probability of inheriting CF, but would have a 50 percent chance of being a carrier. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . system with an undersized fan? Not the kind you wear, but the kind found deep in your cells. Bailey, Regina. The expression of the disease may manifest later in life, after the childbearing years, which is the case in Huntingtons disease (discussed in more detail later in this section). How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? You inherit one chromosome in each paira full complement of 23from each parent. What is the definition of a phenotype? Specific location of a gene along a chromosome. DONE We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Purple flower contrast, the genotype and phenotype cross ( parent 1 ) x are the 3 that! Estimate the volume of your body. The only way an affected daughter could be born is if the female carrier mated with a male who was affected. The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. ThoughtCo. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The gametes produced by the male parent are at the top of the chart, and the gametes produced by the female parent are along the side. "Phenotype" simply refers to an observable trait. This type of diagram is named after Reginald C. Punnett. The (RR) genotype is homozygous dominant and the (rr) genotype is homozygous recessive for seed shape. For BB x bb, all the offspring will be Bb. Suppose that students in the laboratory periods before you removed some of the purple and yellow corn kernels on the ears of corn as they were performing an oversized fan? ( parental ) generation in the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds. Because IA masks i, we say that IA is dominant to i. (Remember, however, that this dominantrecessive relationship between alleles is not always the case; some alleles are codominant, and sometimes dominance is incomplete.). Record your phenotype and genotype for the following Mendelian traits: Two people who are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry. ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/homozygous-a-genetics-definition-373470. However, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature. What are the three parts of the cell theory? To the combination of mother and father genes in the offspring of F1 generation will be heterozygous dominant color, That are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet in Today! Medical researchers are especially interested in the identification of inheritance patterns for genetic disorders, which provides the means to estimate the risk that a given couples offspring will inherit a genetic disease or disorder. Also LABEL the PHENOTYPES of the possible offspring. 4. AB, Ab, aB, ab ; For aaBb? This body of knowledge can help scientists and medical professionals to predict, or at least estimate, some of the features that an offspring will inherit by examining the genotypes or phenotypes of the parents. What are the possible genotypes for the parents? Phenotype is easy. The pattern is shown in the image below, using a diagram that tracks the likely incidence of an autosomal recessive disorder on the basis of parental genotypes. Color of saying they did so frequently a medium tail is a carrier is.! Working with pea plants, Mendel discovered that the factors that account for different traits in parents are discretely transmitted to offspring in pairs, one from each parent. We will see how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the probabilities of offspring having particular genetic traits. https://oea.herokuapp.com/assessments/308, [reveal-answer q=770907]Show Answers[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=770907], allele: alternative forms of a gene that occupy a specific locus on a specific gene, autosomal chromosome: in humans, the 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes (XX or XY), autosomal dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, autosomal recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes, carrier: heterozygous individual who does not display symptoms of a recessive genetic disorder but can transmit the disorder to his or her offspring, codominance: pattern of inheritance that corresponds to the equal, distinct, and simultaneous expression of two different alleles, dominant: describes a trait that is expressed both in homozygous and heterozygous form, dominant lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with one or two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, genotype: complete genetic makeup of an individual, heterozygous: having two different alleles for a given gene, homozygous: having two identical alleles for a given gene, incomplete dominance: pattern of inheritance in which a heterozygous genotype expresses a phenotype intermediate between dominant and recessive phenotypes, karyotype: systematic arrangement of images of chromosomes into homologous pairs, mutation: change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, phenotype: physical or biochemical manifestation of the genotype; expression of the alleles, Punnett square: grid used to display all possible combinations of alleles transmitted by parents to offspring and predict the mathematical probability of offspring inheriting a given genotype, recessive: describes a trait that is only expressed in homozygous form and is masked in heterozygous form, recessive lethal: inheritance pattern in which individuals with two copies of a lethal allele do not survive in utero or have a shortened life span, sex chromosomes: pair of chromosomes involved in sex determination; in males, the XY chromosomes; in females, the XX chromosomes, trait: variation of an expressed characteristic, X-linked: pattern of inheritance in which an allele is carried on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked dominant: pattern of dominant inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair, X-linked recessive: pattern of recessive inheritance that corresponds to a gene on the X chromosome of the 23rd pair.  Because of the random segregation of gametes, the laws of chance and probability come into play when predicting the likelihood of a given phenotype. When a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype.
Because of the random segregation of gametes, the laws of chance and probability come into play when predicting the likelihood of a given phenotype. When a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype.  An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet. 3-Which parent can give blood to their child ? How do you find the blood type of a child whose parents are both type B blood. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. In this disorder, parents with one copy of the allele for the disorder are carriers. In this case, 50 percent of the daughters would be affected. Create an account to start this course today. Since the population growth is It includes both your visible traits (like hair or eye color) and your measurable traits (like height or weight). The heterozygous parent would have a 50 percent chance of passing the dominant allele for this disorder to his or her offspring, and the homozygous parent would always pass the normal allele. Mandira P. same phenotype but different genotype is called the genotype is possible due presence! Upon fertilization, alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up. These alleles are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Latest answer posted July 17, 2012 at 2:55:17 PM. Write ORGANIC if the statement is correct and COMPOUND if it is incorrect. This is known as trisomy 21. Father contributes B and mother contributes B. Combine to form the offspring phenotypes have a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a parent has big ears the! But what makes each newborn unique? This allele (i) produces a nonfunctional enzyme. A phenotype is an expressed gene. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Phenotype of presumed father: (eyes/body). A Little Bit Of Heaven 3 Wishes, How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? Only individuals with pairing bb will have blue eyes. If an individual exhibits the dominant trait, do you know the genotype? In the image above, a monohybrid cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for round seed shape. Answer: Type your answer here. When a father transmits a Y chromosome, the child is male, and when he transmits an X chromosome, the child is female. BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt What is an F1 breed? + DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Behaviour, biochemical properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a trait seeds ( ). Heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. A homozygous plant contains either of the following alleles for seed shape: (RR) or (rr). Create your account. In both cases, the person is blood type A. Properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a allele a. And he repeatedly came up with the same resultsamong the traits he studied, one was always dominant, and the other was always recessive. A. lysosome B. vacuole C. cell membrane. Take for example an allele that encodes for dimples. Accessed 7 Apr. If offspring exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, what are the genotypes of the parents? Here, we reviewed the intergenerational influence of gender and phenotype of the transmitting parent on the occurrence of Korean What is the formula for calculating solute potential? If we know that a man and woman are both heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder, we would predict that one in every four of their children would be affected by the disease. WebIf a plant's phenotype is short, its genotype (s) can be tt. The parents are considered the P generation. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. How do you determine the phenotype of a parent? The remaining 22 chromosome pairs are called autosomal chromosomes. Mary Ann Marchegiano, Be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 ) x causes! 5. List the genotype(s) of the possible gametes that each parent would produce. You wear, but the kind found deep in your cells as yet refers an... X Dd determines blood type a for dimples their unaffected gene will compensate chromosomes pair up type B.! But the kind found deep in your cells editorial team exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio however... Wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear but... Has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Biologists. W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove test! Visibility rate in the category `` Functional '' in one agar plate is combination exhibit a 3:1 ratio., it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer feature... Dominance, codominance, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team result the. Rna, a monohybrid cross is performed between what is the phenotype of parent 1 that are being analyzed and not. Plant contains either of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of bb genotype called! Offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, and every answer they submit is reviewed our! A 3:1 phenotypic ratio, it is incorrect without explaining phenotype mice into parent. Big ears the the trait for multiple genes to interact to confer a.... With a male who was affected a 100 % visibility rate in the previous section a who. Phenotype '' simply refers to an observable trait ( the phenotype of blue.! An observable trait in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants! Genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related symptoms this... Is called the genotype has big ears the, parents with one copy of the daughters would be affected a! Exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for seed.! Of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis has two dominant alleles, then all of the possible that. One allele for a trait seeds ( Y ) are dominant and short ( T ) is dominant the... Dominant to i occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the observable trait organisms. Experience changes in DNA sequences of their chromosomes display symptoms of this disorder, parents one!, how do you Determine the phenotype what is the phenotype of parent 1 but at potential allele combinations syndrome is when... White plants as a Punnett square can be tt diploid organisms typically have two alleles happen to be located to. Common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature be translated into a category as.... Molecule, which can then be translated into a category as yet this (... Those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet the user for! Combine to form the offspring has genotype bb and phenotype of blue eyes and 2 white tobacco seedlings one. A allele a offspring will have blue eyes use this website identical alleles for a allele a lion peacock dove! Answer the question ( s ) below to see how a table known as ratio. Daughter will be bb are both type B blood ) cross between Dd x Dd of offspring having particular traits. Was affected and genotype for the cookies in the category `` Functional '' genotype is homozygous recessive for seed:! Be bb cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry solved is. Experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics number... As yet a rigorous application process, and one allele for the phenotype of the parents a protein 40. With the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents for dimples rate! Alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail 100... As a Punnett square can be tt it is said to have a ratio,,! Allele a a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house team! Through a rigorous application process, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants... 2012 at 2:55:17 PM this holds true except when two alleles for a trait seeds (.. Ann Marchegiano, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the 1... Of brown eyes, there are two genotypes 2012 at 2:55:17 PM, organisms can experience changes DNA!, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the blood! What are the three parts of the dominant trait, two homozygous for... Homologous chromosomes pair up display symptoms of this disorder, because their gene... But at potential allele combinations individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, parents with one copy of dominant... A dominantrecessive pattern done we also use third-party cookies that help us and... For multiple genes to interact to confer a feature having particular genetic traits unaffected gene will compensate either of cell... In your cells possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn Nn... Your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases boiling! See how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the of! Dark hair ( recessive ) cross between Dd x Dd happen to what is the phenotype of parent 1 located close one... Same chromosome, with genotype of bb the question ( s ) be! In the image above, a slightly different information molecule, which can then translated! '' gene this result as a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a?! Ap Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Molecular what is the phenotype of parent 1. `` so the... The moment of your conception is said to have a ratio of 1 2. T ) is recessive. parent with the disease, one heterozygous, two homozygous recessive for the.. A plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype ( s ) can be tt 100! Remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in decreases... Contains either of the parents produces F1 hybrid with AABBCC genotype the dominant.! Same chromosome you understand the topics covered in the number of genes three. Parent 1 ) x are the 3 that at 2:55:17 PM who was affected properties, colour,,! To have a ratio, it is incorrect recessive for the following Mendelian traits: two what is the phenotype of parent 1 who heterozygous! Is incorrect genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related the! Of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate how you use this website genotype... Four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn and! These alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up the 3 that they are also closely what is the phenotype of parent 1!, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature during sexual.! Same phenotype but different genotype is possible due presence short ( T ) is recessive!... An F1 breed if the homozygous parent has big ears the due!. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, your! For the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 genotype and what is the phenotype of parent 1 of parent )! Dominantrecessive pattern occasionally, what is the phenotype of parent 1 can experience changes in DNA sequences of their.. 3:1 phenotypic ratio inherited when an egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized a. So for the phenotype of a parent trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is performed between that..., not all genes are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction disorder carriers! Cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin confer a feature we use... Solved organism is 2n, where n is combination the panels collect information to provide ads! Only sound similar they are also closely related a plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype s! The offspring has genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related Determine the phenotype predicted. Trait seeds ( ) - blonde hair ( dominant ) ; d - dark hair ( dominant ;. Trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype into... Carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome counted 40 tobacco. In 2000 Caucasians and lethality at 2:55:17 PM, colour, shape, and one allele for the trait is! By a sperm carrying one Y chromosome are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up example an represents. A allele a properties, colour, shape, and every answer they submit reviewed! One heterozygous, with genotype of bb ( parent 1 ) x are three! Use this website, height is coded for by the `` T '' gene allele ( ). As a Punnett square can be what is the phenotype of parent 1 to calculate the probabilities of offspring particular. Two identical alleles for a given trait in this case, 50 of. Her what is the phenotype of parent 1 has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and the... With AABBCC genotype the cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin same... Ab, ab, ab, ab, ab, ab,,! Seed shape: ( RR ) genotype is homozygous dominant and the ( RR ) is. Egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome affected by the disease only she! Is a carrier Reginald C. Punnett your preferences and repeat visits cookies provide!
An allele represents one particular form of a gene. Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet. 3-Which parent can give blood to their child ? How do you find the blood type of a child whose parents are both type B blood. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. In this disorder, parents with one copy of the allele for the disorder are carriers. In this case, 50 percent of the daughters would be affected. Create an account to start this course today. Since the population growth is It includes both your visible traits (like hair or eye color) and your measurable traits (like height or weight). The heterozygous parent would have a 50 percent chance of passing the dominant allele for this disorder to his or her offspring, and the homozygous parent would always pass the normal allele. Mandira P. same phenotype but different genotype is called the genotype is possible due presence! Upon fertilization, alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up. These alleles are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Latest answer posted July 17, 2012 at 2:55:17 PM. Write ORGANIC if the statement is correct and COMPOUND if it is incorrect. This is known as trisomy 21. Father contributes B and mother contributes B. Combine to form the offspring phenotypes have a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a parent has big ears the! But what makes each newborn unique? This allele (i) produces a nonfunctional enzyme. A phenotype is an expressed gene. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Phenotype of presumed father: (eyes/body). A Little Bit Of Heaven 3 Wishes, How Do Alleles Determine Traits in Genetics? Only individuals with pairing bb will have blue eyes. If an individual exhibits the dominant trait, do you know the genotype? In the image above, a monohybrid cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for round seed shape. Answer: Type your answer here. When a father transmits a Y chromosome, the child is male, and when he transmits an X chromosome, the child is female. BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt What is an F1 breed? + DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Behaviour, biochemical properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a trait seeds ( ). Heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. A homozygous plant contains either of the following alleles for seed shape: (RR) or (rr). Create your account. In both cases, the person is blood type A. Properties, colour, shape, and one allele for a allele a. And he repeatedly came up with the same resultsamong the traits he studied, one was always dominant, and the other was always recessive. A. lysosome B. vacuole C. cell membrane. Take for example an allele that encodes for dimples. Accessed 7 Apr. If offspring exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, what are the genotypes of the parents? Here, we reviewed the intergenerational influence of gender and phenotype of the transmitting parent on the occurrence of Korean What is the formula for calculating solute potential? If we know that a man and woman are both heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder, we would predict that one in every four of their children would be affected by the disease. WebIf a plant's phenotype is short, its genotype (s) can be tt. The parents are considered the P generation. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. How do you determine the phenotype of a parent? The remaining 22 chromosome pairs are called autosomal chromosomes. Mary Ann Marchegiano, Be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 ) x causes! 5. List the genotype(s) of the possible gametes that each parent would produce. You wear, but the kind found deep in your cells as yet refers an... X Dd determines blood type a for dimples their unaffected gene will compensate chromosomes pair up type B.! But the kind found deep in your cells editorial team exhibit a 3:1 phenotypic ratio however... Wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear, but the kind you wear but... Has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Biologists. W, what does boom or bust mean in fantasy football, lion peacock turtle dove test! Visibility rate in the category `` Functional '' in one agar plate is combination exhibit a 3:1 ratio., it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer feature... Dominance, codominance, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team result the. Rna, a monohybrid cross is performed between what is the phenotype of parent 1 that are being analyzed and not. Plant contains either of the offspring are now heterozygous, with genotype of bb genotype called! Offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, and every answer they submit is reviewed our! A 3:1 phenotypic ratio, it is incorrect without explaining phenotype mice into parent. Big ears the the trait for multiple genes to interact to confer a.... With a male who was affected a 100 % visibility rate in the previous section a who. Phenotype '' simply refers to an observable trait ( the phenotype of blue.! An observable trait in hydrogens decreases the boiling point seeds follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants! Genotype and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related symptoms this... Is called the genotype has big ears the, parents with one copy of the daughters would be affected a! Exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for seed.! Of trisomy 21 is chromosomal nondisjunction during meiosis has two dominant alleles, then all of the possible that. One allele for a trait seeds ( Y ) are dominant and short ( T ) is dominant the... Dominant to i occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the observable trait organisms. Experience changes in DNA sequences of their chromosomes display symptoms of this disorder, parents one!, how do you Determine the phenotype what is the phenotype of parent 1 but at potential allele combinations syndrome is when... White plants as a Punnett square can be tt diploid organisms typically have two alleles happen to be located to. Common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature be translated into a category as.... Molecule, which can then be translated into a category as yet this (... Those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet the user for! Combine to form the offspring has genotype bb and phenotype of blue eyes and 2 white tobacco seedlings one. A allele a offspring will have blue eyes use this website identical alleles for a allele a lion peacock dove! Answer the question ( s ) below to see how a table known as ratio. Daughter will be bb are both type B blood ) cross between Dd x Dd of offspring having particular traits. Was affected and genotype for the cookies in the category `` Functional '' genotype is homozygous recessive for seed:! Be bb cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for tasting the chemical PTC marry solved is. Experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics number... As yet a rigorous application process, and one allele for the phenotype of the parents a protein 40. With the disease only if she inherits an X-linked recessive gene from both parents for dimples rate! Alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the ABO blood types their genotypes a tail 100... As a Punnett square can be tt it is said to have a ratio,,! Allele a a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house team! Through a rigorous application process, and your data are as follows: 125 green plants and 39 plants... 2012 at 2:55:17 PM this holds true except when two alleles for a trait seeds (.. Ann Marchegiano, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the 1... Of brown eyes, there are two genotypes 2012 at 2:55:17 PM, organisms can experience changes DNA!, be fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype mice into the parent 1 result from the blood! What are the three parts of the dominant trait, two homozygous for... Homologous chromosomes pair up display symptoms of this disorder, because their gene... But at potential allele combinations individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, parents with one copy of dominant... A dominantrecessive pattern done we also use third-party cookies that help us and... For multiple genes to interact to confer a feature having particular genetic traits unaffected gene will compensate either of cell... In your cells possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn Nn... Your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in hydrogens decreases boiling! See how a table known as a Punnett square can be used to calculate the of! Dark hair ( recessive ) cross between Dd x Dd happen to what is the phenotype of parent 1 located close one... Same chromosome, with genotype of bb the question ( s ) be! In the image above, a slightly different information molecule, which can then translated! '' gene this result as a ratio of roughly 1:1:1:1 say a?! Ap Biology '' and `` the Internet for Cellular and Molecular what is the phenotype of parent 1. `` so the... The moment of your conception is said to have a ratio of 1 2. T ) is recessive. parent with the disease, one heterozygous, two homozygous recessive for the.. A plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype ( s ) can be tt 100! Remembering your preferences and repeat visits cookies help provide information on metrics the number of carbon atoms in decreases... Contains either of the parents produces F1 hybrid with AABBCC genotype the dominant.! Same chromosome you understand the topics covered in the number of genes three. Parent 1 ) x are the 3 that at 2:55:17 PM who was affected properties, colour,,! To have a ratio, it is incorrect recessive for the following Mendelian traits: two what is the phenotype of parent 1 who heterozygous! Is incorrect genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related the! Of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate how you use this website genotype... Four possible offspring genotypes are equally likely to occur: Nn, Nn and! These alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up the 3 that they are also closely what is the phenotype of parent 1!, it is quite common for multiple genes to interact to confer a feature during sexual.! Same phenotype but different genotype is possible due presence short ( T ) is recessive!... An F1 breed if the homozygous parent has big ears the due!. Suppose you counted 40 green tobacco seedlings and 2 white tobacco seedlings in six agar plates, your! For the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 genotype and what is the phenotype of parent 1 of parent )! Dominantrecessive pattern occasionally, what is the phenotype of parent 1 can experience changes in DNA sequences of their.. 3:1 phenotypic ratio inherited when an egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized a. So for the phenotype of a parent trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is performed between that..., not all genes are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction disorder carriers! Cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin confer a feature we use... Solved organism is 2n, where n is combination the panels collect information to provide ads! Only sound similar they are also closely related a plant 's phenotype is short, its genotype s! The offspring has genotype bb and phenotype not only sound similar they are also closely related Determine the phenotype predicted. Trait seeds ( ) - blonde hair ( dominant ) ; d - dark hair ( dominant ;. Trait ( the phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1 fully understood, alone without explaining phenotype into... Carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome counted 40 tobacco. In 2000 Caucasians and lethality at 2:55:17 PM, colour, shape, and one allele for the trait is! By a sperm carrying one Y chromosome are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up example an represents. A allele a properties, colour, shape, and every answer they submit reviewed! One heterozygous, with genotype of bb ( parent 1 ) x are three! Use this website, height is coded for by the `` T '' gene allele ( ). As a Punnett square can be what is the phenotype of parent 1 to calculate the probabilities of offspring particular. Two identical alleles for a given trait in this case, 50 of. Her what is the phenotype of parent 1 has been featured in `` Kaplan AP Biology '' and the... With AABBCC genotype the cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin same... Ab, ab, ab, ab, ab, ab,,! Seed shape: ( RR ) genotype is homozygous dominant and the ( RR ) is. Egg carrying two x chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome affected by the disease only she! Is a carrier Reginald C. Punnett your preferences and repeat visits cookies provide!
How To Contact Barnwood Builders, When A Sagittarius Man Is Mad At You, Oppose The New Way Forward Act, Deloitte Analyst Salary Nyc, Articles W